News
News

The visit of the President of the AASc Elchin Khalilov to Kazakhstan marked the beginning of successful cooperation between the Asian Academy of Sciences and scientific and educational institutions of Kazakhstan.
December 24, 2025
On December 22-23, 2025, Professor Elchin Khalilov, President of the Asian Academy of Sciences (AAS), visited the Republic of Kazakhstan to discuss avenues for cooperation between the AAS and Kazakh scientific and educational institutions.
The visit featured a working meeting on December 22 between Academician Elchin Khalilov and the Rector of Astana International University, Professor Serik Irsaliyev, who is also a Doctor of Philosophy and an AAS Academician. The meeting was attended by:
Karlygash Nugmanova, AAS Academician and Presidium Member, Chair of the AAS Section on Political Science and International Relations, Professor, Doctor of Political Sciences;
Farid Khalilov, AAS Executive Director and Chair of the International Relations Committee;
Anar Murzagaliyeva, First Vice-President of Astana International University;
Kairat Abdrakhmanov, Vice-President of Astana International University.
The parties discussed key priorities for cooperation between the Asian Academy of Sciences and Astana International University.
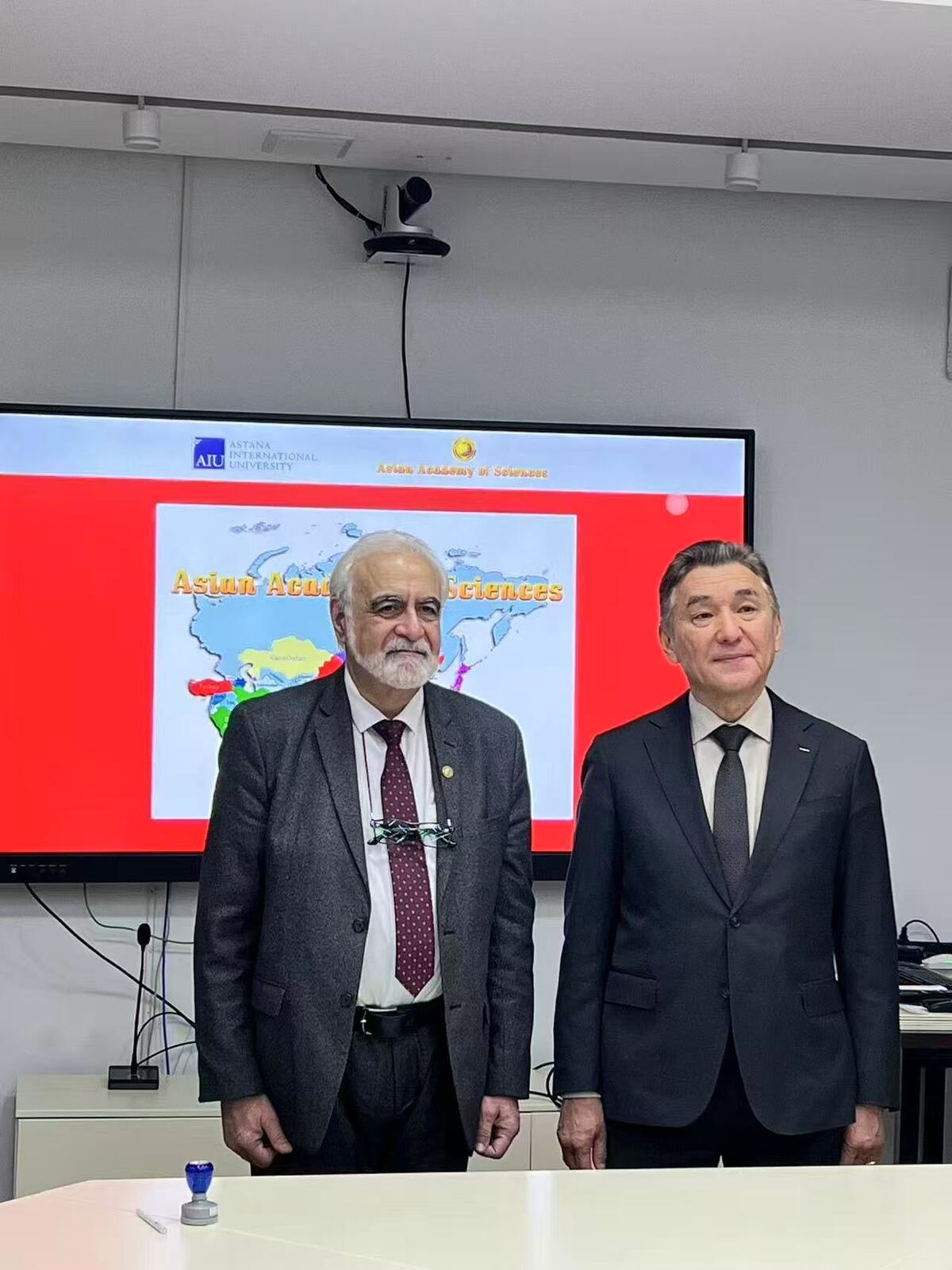

From left to right: President of the Asian Academy of Sciences Elchin Khalilov and President of Astana International University Serik Irsaliev
Following the negotiations, a Memorandum of Cooperation was signed between the Asian Academy of Sciences and Astana International University.
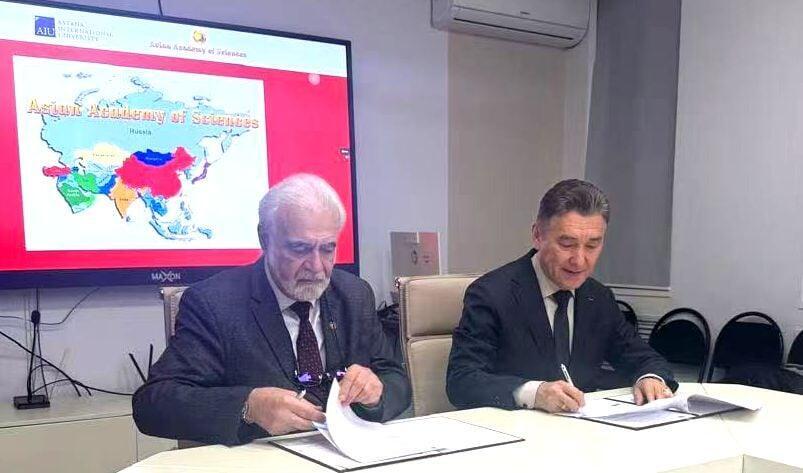

The moment of signing the memorandum of cooperation between the Asian Academy of Sciences and Astana International University.

The President of the Academy of Sciences, Academician Elchin Khalilov, and the President of Astana International University, Academician Serik Irsaliev, exchange signed memorandums of cooperation.
On December 23, 2025, Academician Elchin Khalilov held another meeting with Professor Yerlan Sydykov, Rector of the L.N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University (ENU) and a Doctor of Historical Sciences. The discussions focused on potential cooperation between the Asian Academy of Sciences (AAS) and ENU in the fields of science and education.
The meeting was also attended by:
Syrym Sharipkhanov, Vice-President of the Academy of Military Sciences of the Republic of Kazakhstan, AAS Academician, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor, retired Major General, Head of the Kazakh Research and Training Center for Civil Protection and Labor Safety (former Minister of Emergency Situations of the Republic of Kazakhstan);
Farid Khalilov, AAS Executive Director and Chair of the International Relations Committee;
Yerlan Sabitov, Dean of the Faculty of Architecture and Civil Engineering, Candidate of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor;
Erik Nurmoldin, Dean of the Faculty of Physics and Technology, Candidate of Physical and Mathematical Sciences;
Zharas Berdenov, Dean of the Faculty of Natural Sciences, Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.), Associate Professor.
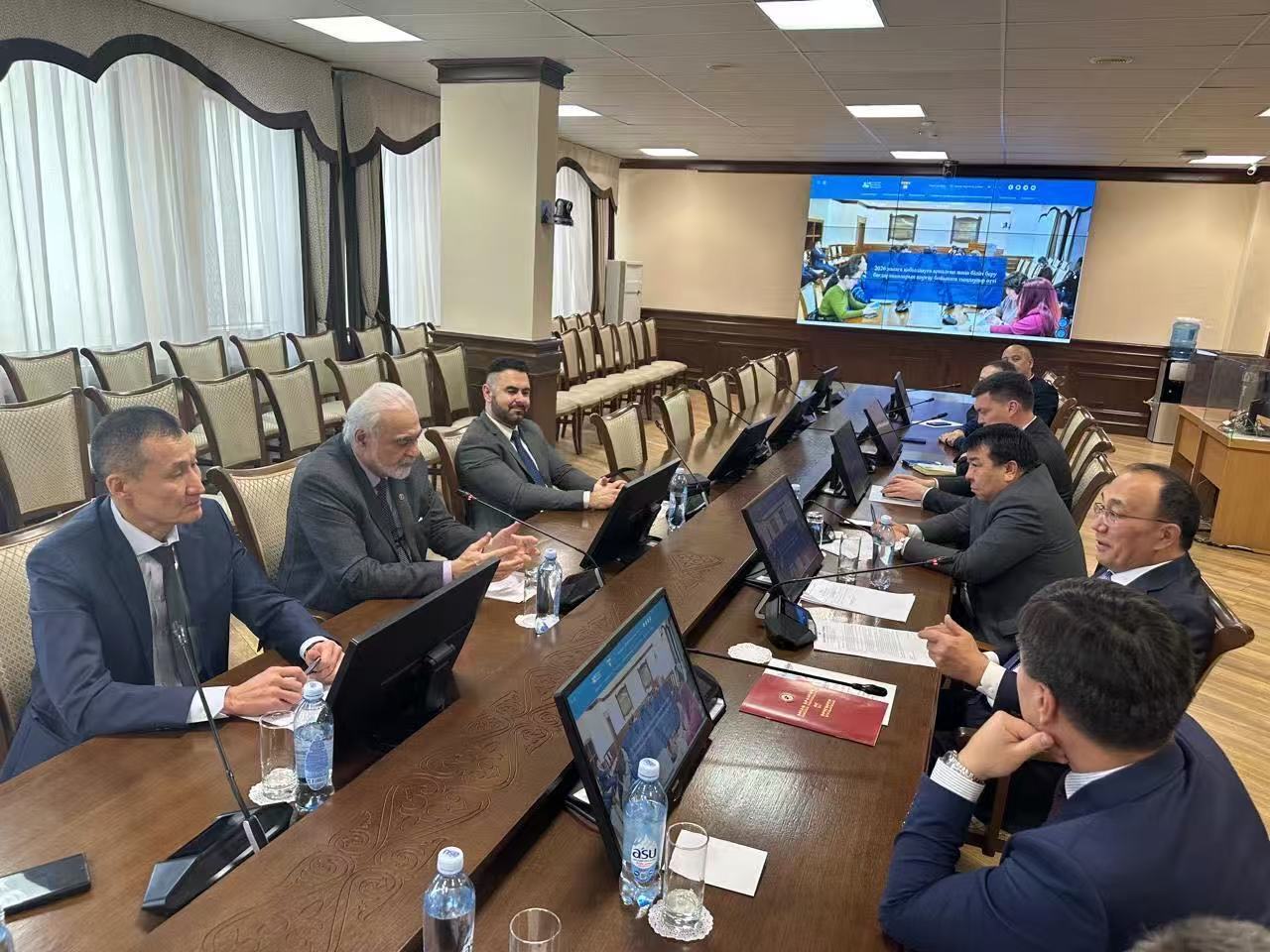

In the photo, the moment of discussion of cooperation in the field of science and education between President of the Asian Academy of Sciences Elchin Khalilov and Rector of the L. N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, Professor, Doctor of Historical Sciences Yerlan Sydykov.
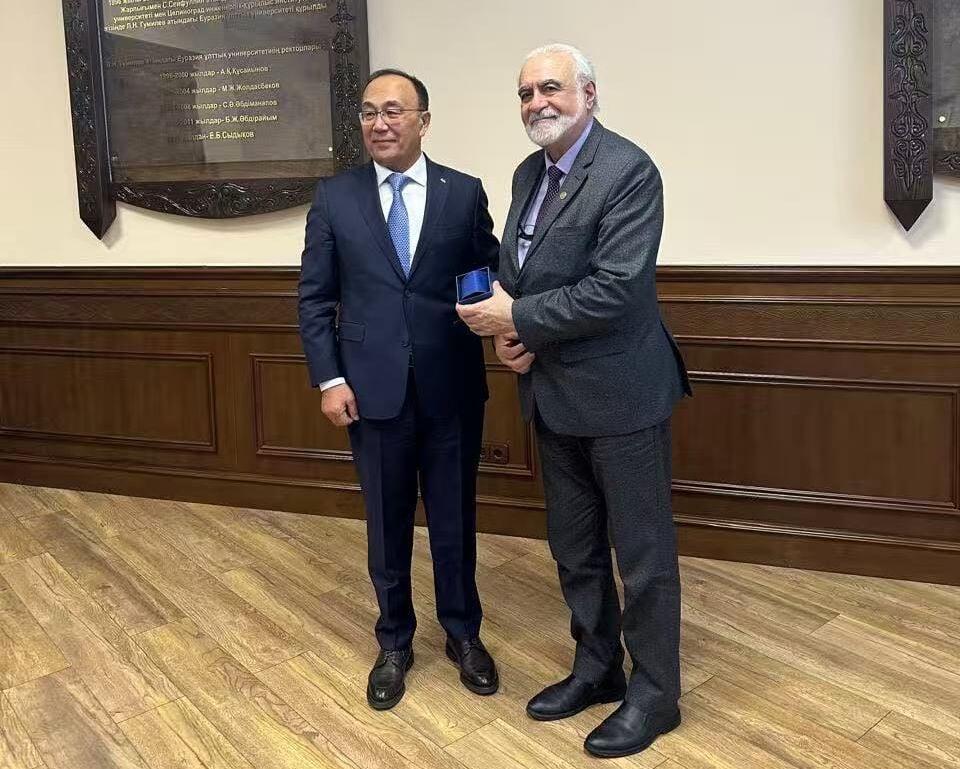

From left to right: Rector of the L. N. Gumilyov Eurasian National University, Professor Yerlan Sydykov and President of the Asian Academy of Sciences, Academician Elchin Khalilov.
A subsequent meeting was held with the research team of the "Kazakhstan Engineering" R&D Center. During the meeting, Professor Elchin Khalilov, President of the Asian Academy of Sciences (AAS), presented an overview of the AAS, detailing its mission, objectives, organizational structure, and founding history.
In turn, the scientists from the "Kazakhstan Engineering" Center briefed Academician Khalilov on their core activities, key achievements, and ongoing development projects.
The meeting was also attended by:
Alizhan Tulembayev, Deputy General Director of the "Kazakhstan Engineering" Center;
Tatyana Kaiser, Head of the Scientific and Technical Research Department.
Following the exchange of views, the parties agreed to continue and deepen their scientific cooperation.
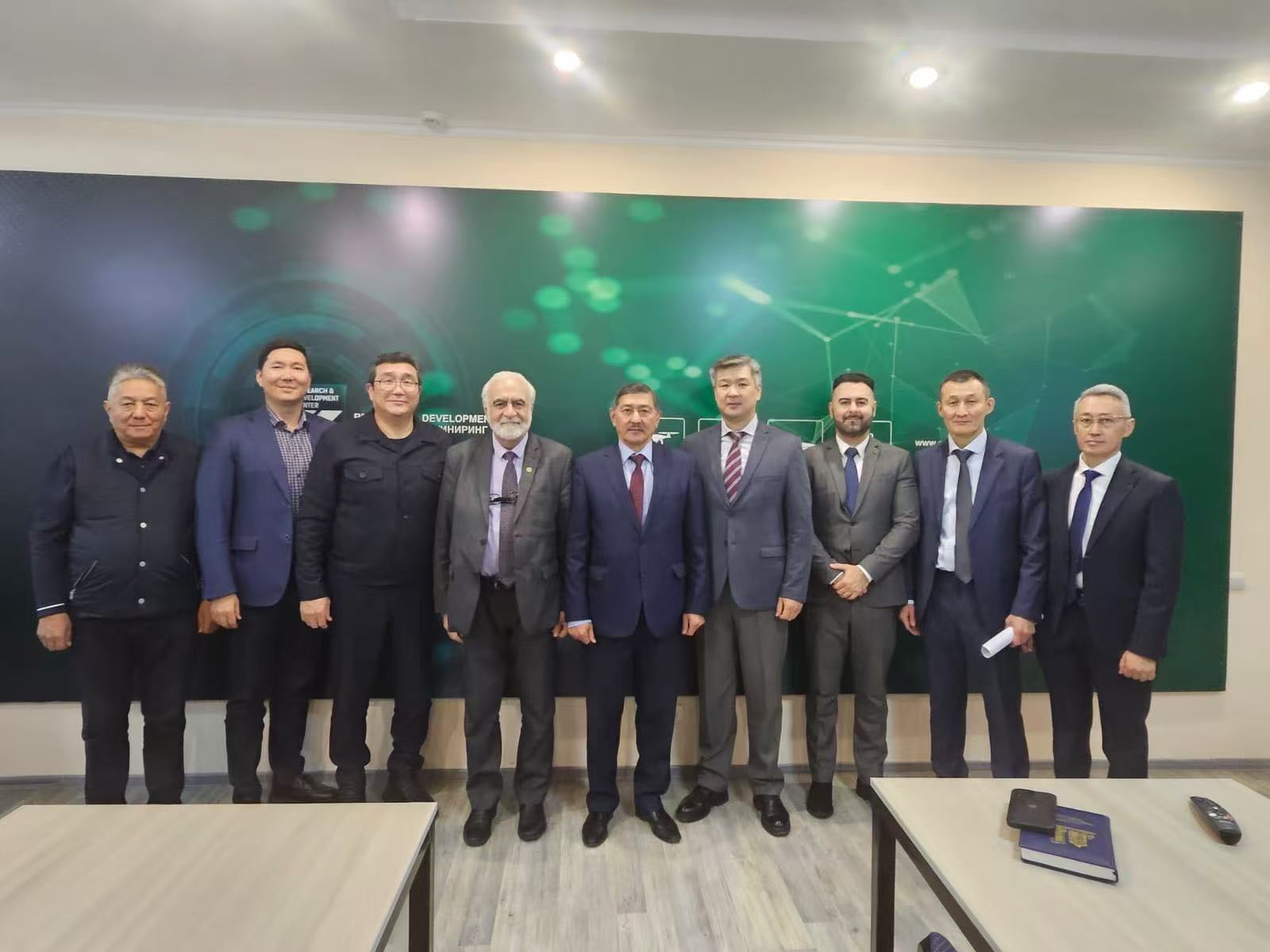

In the photo: President of the AAN Elchin Khalilov and the scientific and management staff of the Kazakhstan Engineering Center.
AASс President Elchin Khalilov Visits Georgia to Sign Historic Cooperation MoU with Georgian Academy of Sciences

December 11–12, 2025, marked a historic official visit by the President of the Asian Academy of Sciences (AAS), Academician Elchin Khalilov, to the Georgian National Academy of Sciences (GNAS), heralding a new chapter in scientific cooperation.
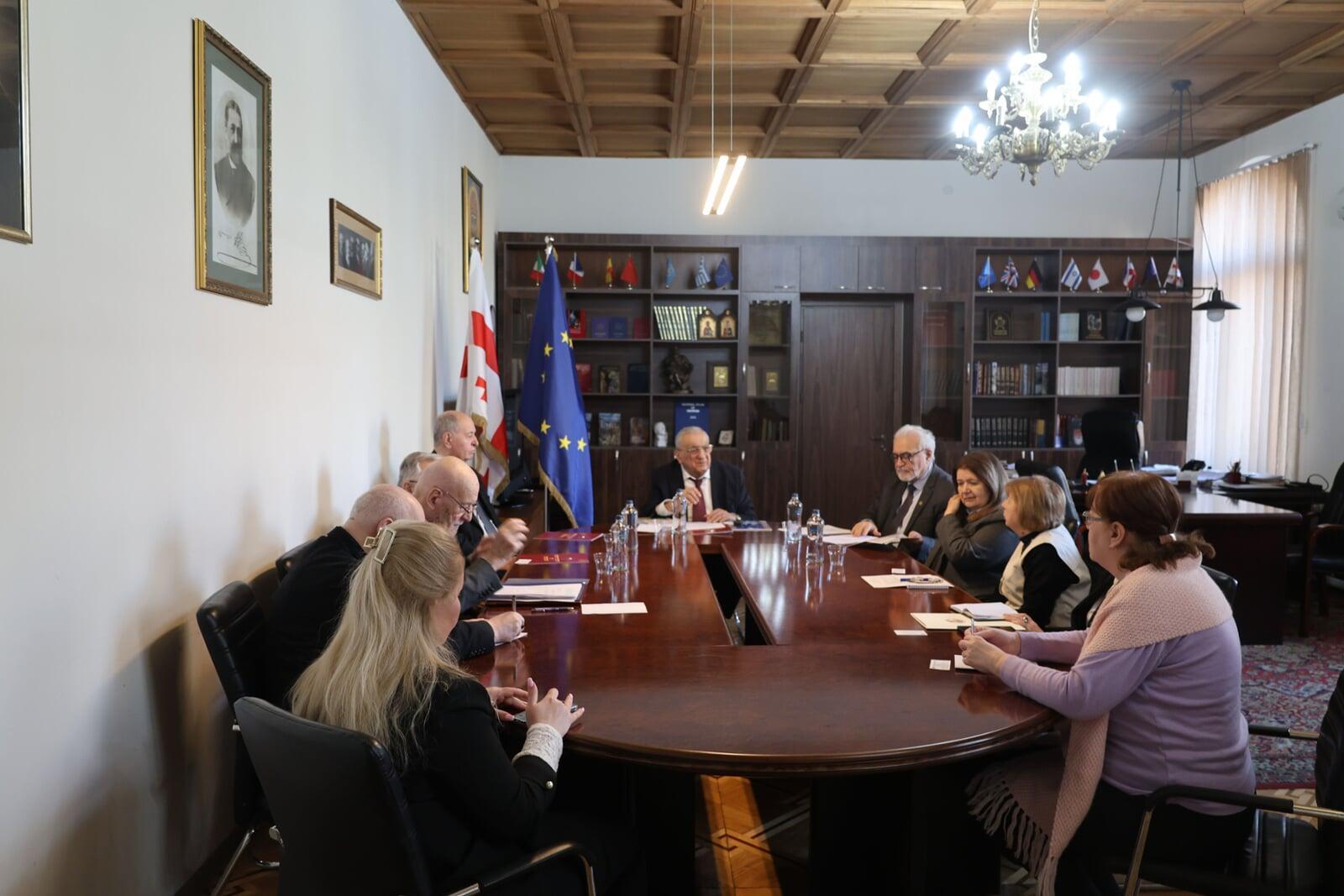

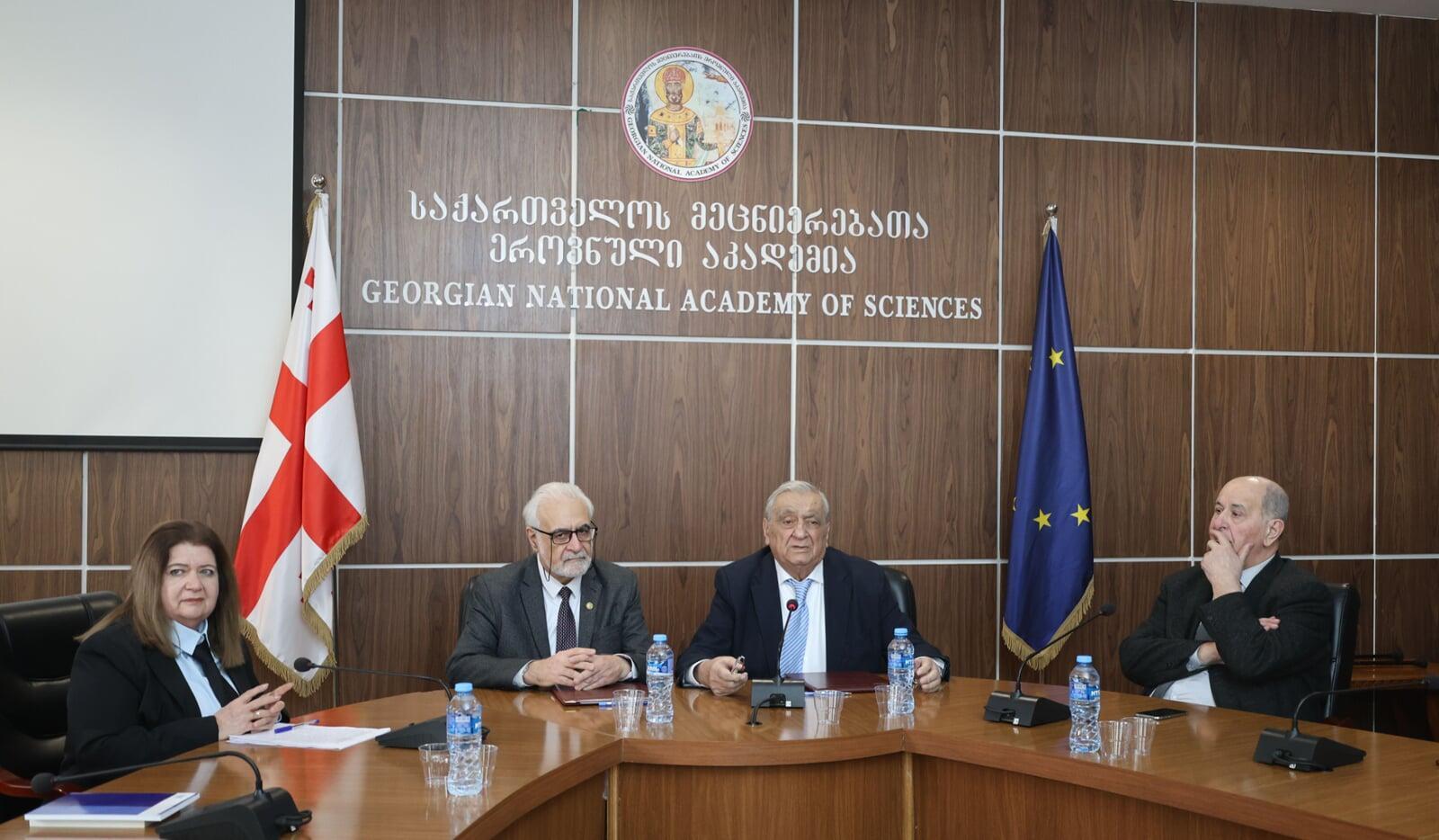
On December 11, a high-level working meeting between the leadership of the two academies was held. The meeting was attended by AAS President Elchin Khalilov, GNAS President Roin Metreveli, Deputy Chair of the AAS Scientific Council and Chair of the Humanities Section, Academician Tamila Khalilova, as well as Vice-Presidents and members of the GNAS Presidium. During substantive discussions, key development vectors for the AAS were outlined, and organizational matters for the Second General Assembly of the Academy, scheduled for 2026 in Beijing, were addressed. Special emphasis was placed on the pivotal role of Asian national academies of sciences in implementing large-scale international scientific programs under the auspices of the AAS. Following the meeting, the text of the Memorandum of Cooperation between the two institutions was unanimously approved.
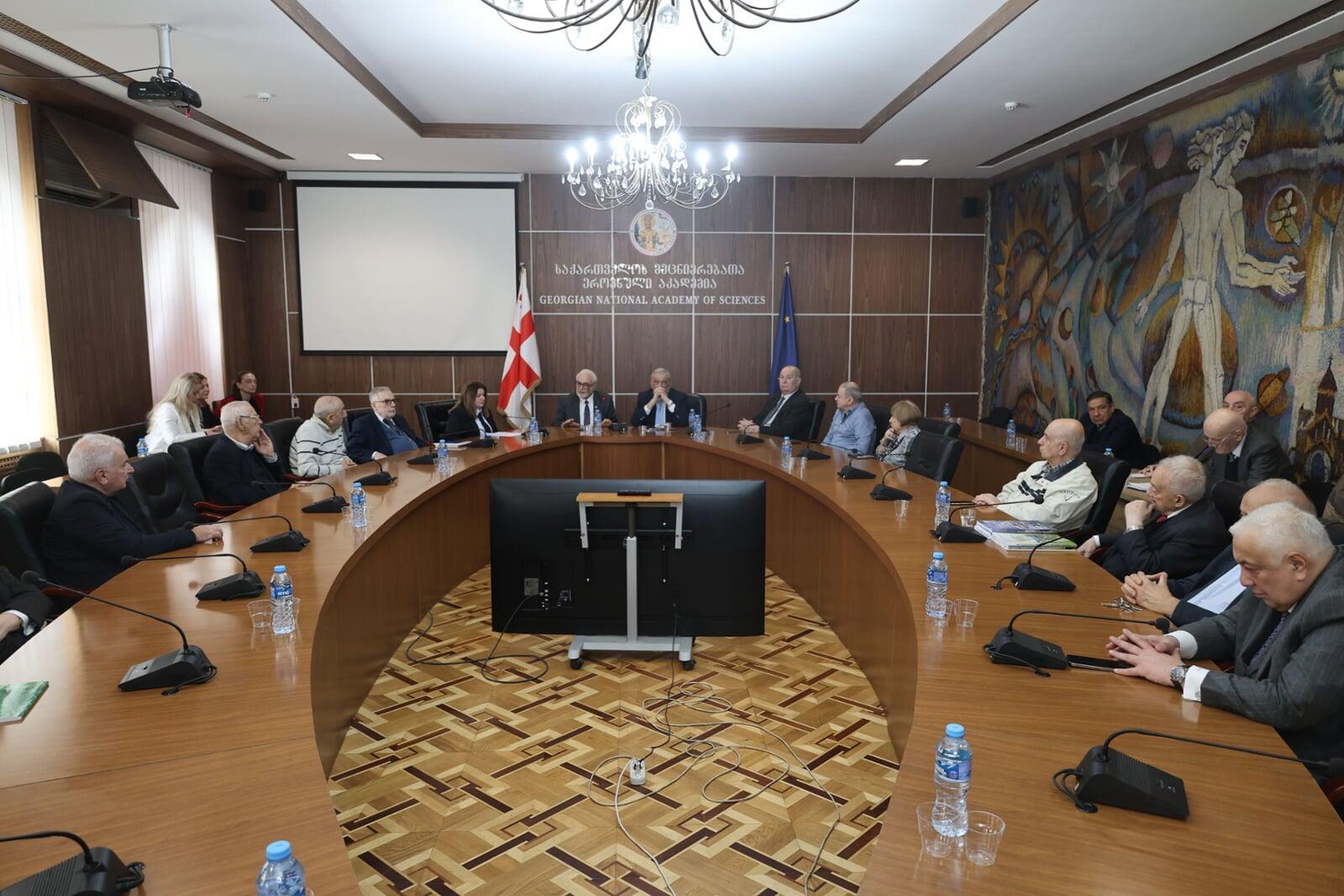
On December 12, the visit featured an expanded meeting of the GNAS Presidium, convening the elite of Georgian science: academicians, rectors of leading universities, and directors of the country's research institutes and scientific institutions.
After the opening addresses by GNAS President Roin Metreveli and AAS President Elchin Khalilov, a solemn ceremony was held for the signing of the historic Memorandum of Cooperation between the Georgian National Academy of Sciences and the Asian Academy of Sciences, establishing a solid legal foundation for long-term partnership.
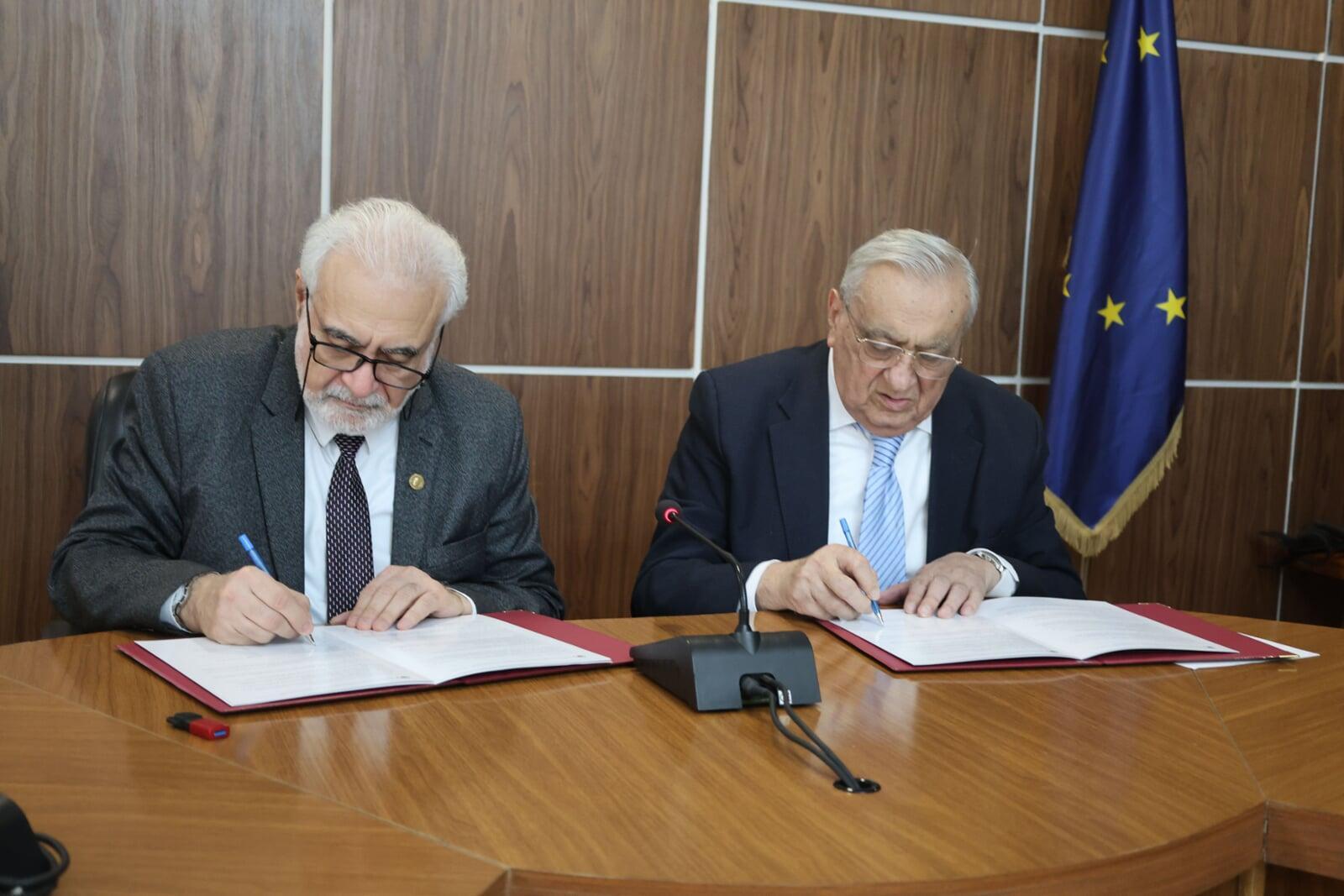
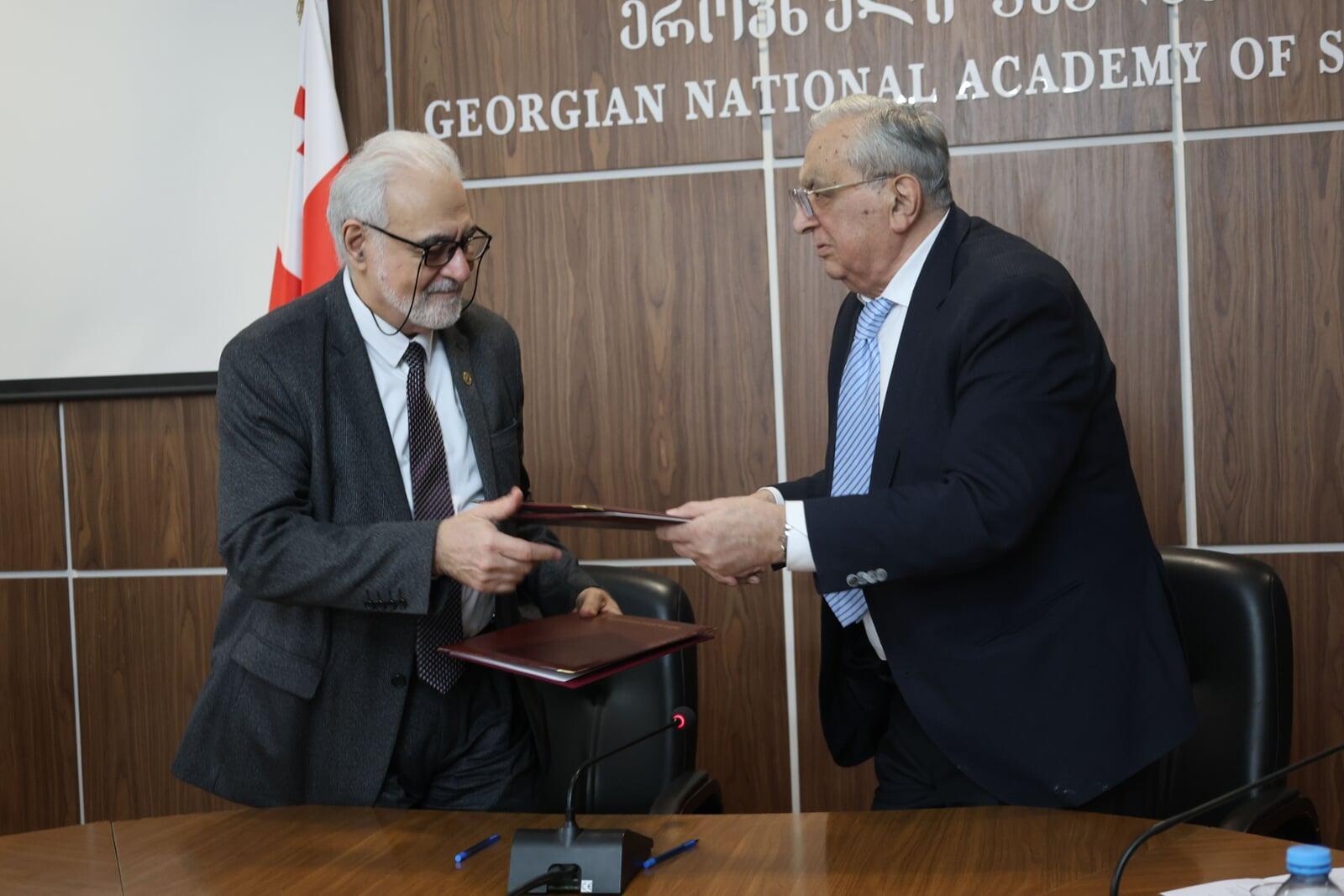



Subsequently, the participants were presented with a scientific lecture on "The Caspian Route of the Silk Road. Historical and Geographical Aspects," delivered by the Deputy Chair of the AAS Scientific Council and Chair of the Humanities Section, Academician Tamila Khalilova. The presentation sparked a lively discussion with participation from members of the GNAS Presidium, academicians, and heads of Georgian scientific and educational institutions.
A key practical outcome was the decision to develop a comprehensive Joint Research Program on this topic, involving scientists from Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and China, marking the launch of the first concrete project under the new alliance.
This visit and the signed Memorandum open broad prospects for deepening scientific dialogue, integrating academic resources, and implementing ambitious joint initiatives across Asia.
The International Scientific Conference
"MODERN CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF ONCOLOGY"
On December 05, 2025, the International Scientific Conference "MODERN CHALLENGES AND PROSPECTS FOR THE DEVELOPMENT OF ONCOLOGY", organized by the Asian Academy of Sciences and the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Bashkortostan, was held in Ufa, Bashkortostan, Russian Federation.
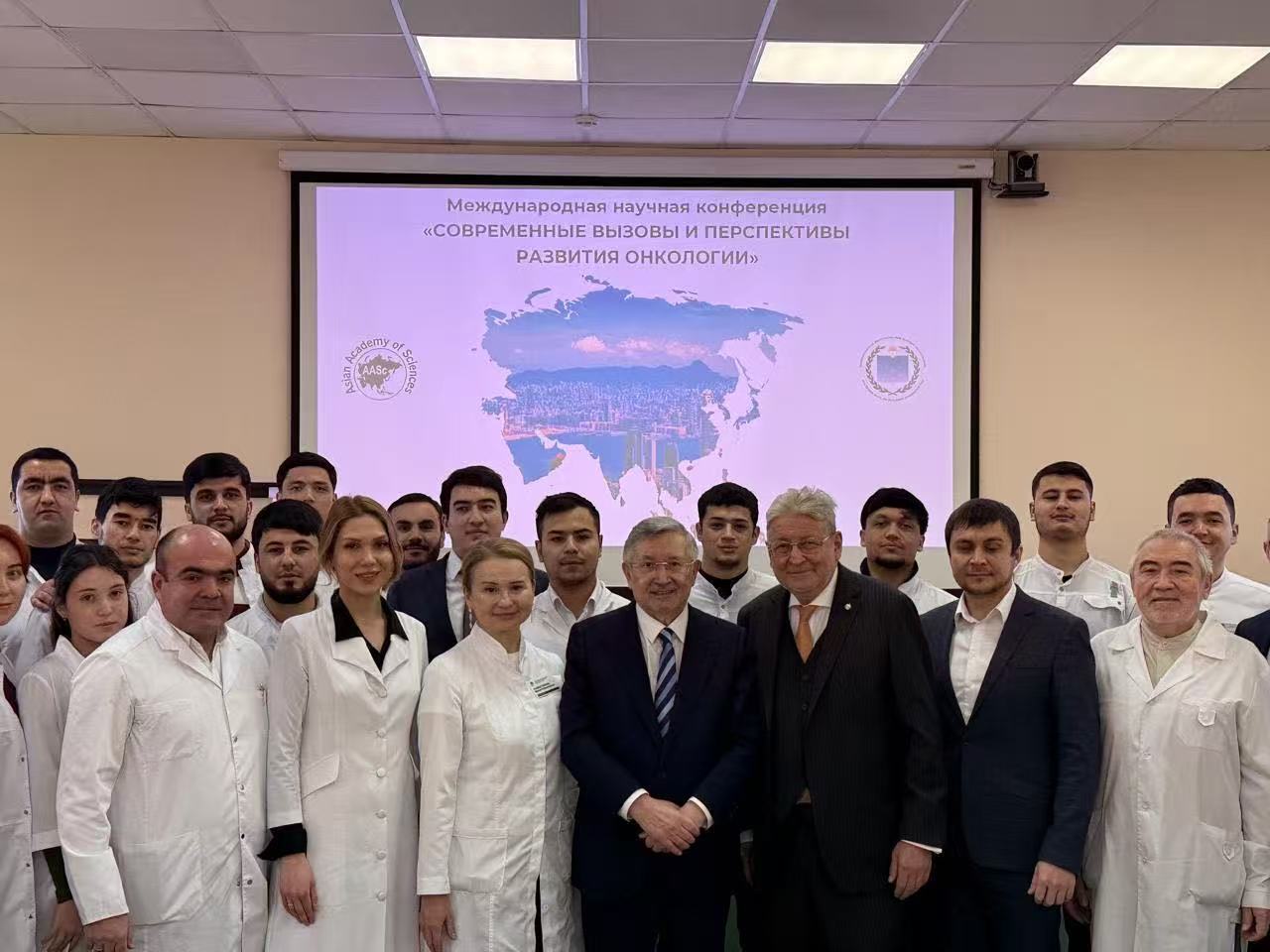


The Director of the Republican Clinical Oncology Dispensary of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Bashkortostan, Academician Shamil Gantsev, and the Secretary General of the Asian Academy of Sciences, Academician Ramil Bakhtizin, are at the center.
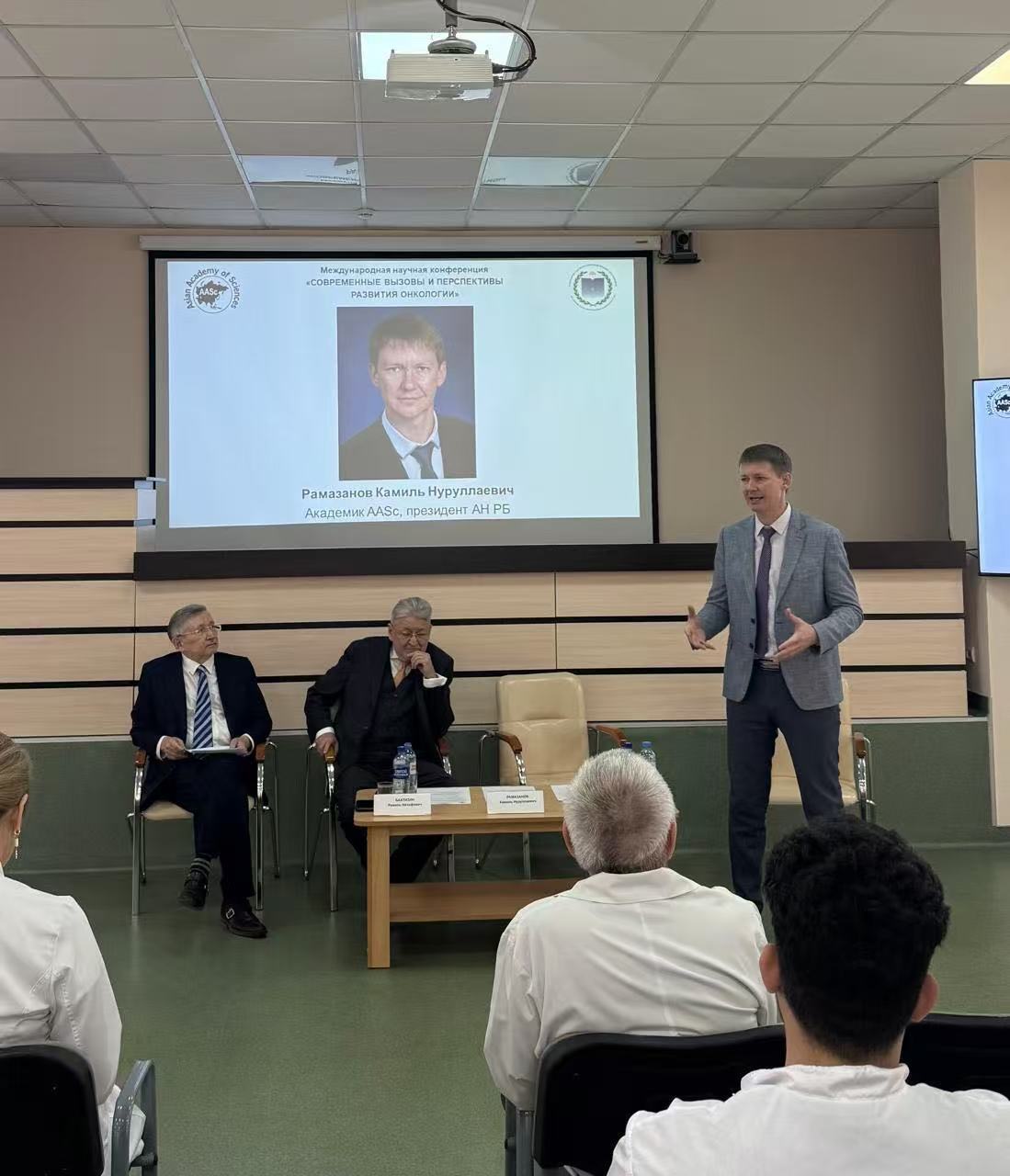

Presentation of the plenary speech by the President of the Academy of Sciences of Bashkortostan, Academician Kamil Ramazanov
First heart transplant from deceased donor performed in Azerbaijan

05.12.2025 AASc News
The Ministry of Health’s Coordination Center for Organ Donation and Transplantation received notification from Sabunchu Medical Center about a patient diagnosed with brain death.
The Coordination Center promptly organized and coordinated the organ donation and transplantation process.
After confirming the brain death diagnosis, the deceased’s family consented to organ donation in a profound act of humanism. As a result, the first heart transplant from a deceased donor in the Caucasus region was successfully performed.
The heart transplant surgery was carried out with high professionalism at the Central Clinic by a specialized medical team led by Chief Physician Professor Kamran Musayev. The heart was transplanted into a resident of Tovuz district born in 2006.
“The Ministry of Health expresses gratitude to the donor’s family for their noble gesture, thanks the medical specialists who performed their duties at the highest level, and wishes them success in their future endeavors,” the statement emphasized.

A New Force in Global Science is Launched in Asia: Outcomes of the Historic First General Assembly of the Asian Academy of Sciences Announced

Press Release, Asian Academy of Sciences (AAS) – 24.11.2025
Hong Kong/Beijing – The Asian Academy of Sciences (AAS), officially registered in Hong Kong on August 12, 2025, as an international non-profit organization, has successfully convened its inaugural General Assembly. This event marks a historic step towards creating a unified academic and intellectual space in Asia (UAISA) – a new platform for scientific cooperation based on the principles of mutual respect, collegiality, and the free exchange of knowledge.
President of the AAS – Elchin Khalilov was elected President. He is a renowned Chinese and Azerbaijani scientist, a National High-End Talent of China, Academician, Professor at Wenzhou University, and recipient of Zhejiang Province's highest award for foreign experts, the "West Lake Friendship Award."
Vice-Presidents of the AAS – Eminent leaders of national academies of sciences and leading scholars from across the continent were elected, underscoring the pan-Asian character and the highest caliber of the organization:
Pansheng Qian (China) – Academician, Professor, Vice-President of the China Association for Industrial Environmental Protection.
Valery Tupolev (Russia) – Academician, Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor, Vice-President of the Russian Academy of Engineering.
Kauser Abdulla Malik (Pakistan) – Academician, Professor, President of the Pakistan Academy of Sciences.
Roin Metreveli (Georgia) – Academician, Doctor of Historical Sciences, Professor, President of the Georgian Academy of Sciences.
Shavkat Ayupov (Uzbekistan) – Academician, Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Professor, President of the Academy of Sciences of Uzbekistan.
Adalat Muradov (Azerbaijan) – Academician, Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, Rector of the Azerbaijan State University of Economics (UNEC).
Kobiljon Khushvakhtzoda (Tajikistan) – Academician, Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, President of the Academy of Sciences of Tajikistan.
Elshan Hajizade (Azerbaijan) – Academician, Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, Head of the Industry and Energy Department of the Cabinet of Ministers of Azerbaijan.
Kanatbek Aziz (Kyrgyzstan) – Corresponding Member of the National Academy of Sciences of the Kyrgyz Republic, Doctor of Sciences, Professor, Director of the Research Institute "Geopolitics and Strategy," Advisor to the First Chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers of the Kyrgyz Republic.
Secretary-General of the AAS – Ramil Bakhtizin (Russia) was elected Secretary-General. He is an Academician, Doctor of Physical and Mathematical Sciences, Professor, and Academic Secretary of the Academy of Sciences of the Republic of Bashkortostan.
Honorary Academicians – World-renowned figures were unanimously elected:
Takaaki Kajita (Japan) – Nobel Laureate in Physics, Distinguished Professor at the University of Tokyo.
Atta-ur-Rahman (Pakistan) – UNESCO Laureate, Academician of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Pakistan Academy of Sciences, former Federal Minister for Science and Technology of Pakistan.
Boris Gusev (Russia) – President of the Russian and International Engineering Academies, Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Laureate of State Prizes.
Olzhas Suleimenov (Kazakhstan) – Poet, public figure, Co-Chairman of the "Assembly of the Peoples of the World," Director of the UNESCO International Centre for the Rapprochement of Cultures.
Akylbek Japarov (Kyrgyzstan) – First Chairman of the Cabinet of Ministers – Head of the Presidential Administration of the Kyrgyz Republic, Doctor of Economic Sciences, Professor, Academician.
Establishment of the Asian Intellectual Property Organization (AIPO) and the Asian Patent Office (APO).
Creation of the Asian Impact Factor Agency (AIFA) for indexing regional scientific journals.
Formation of the Regional Center "Caucasus-Central Asia" (Chairman – Academician Adalat Muradov) and the Asian Institute of Economics (AIE) (Director – Academician Elshan Hajizade).
Launch of new AAS scientific journals – "Asian Economic Science" (Editor-in-Chief – Academician Elshan Hajizade) and "Asia of the Future" (Editor-in-Chief – Academician Emil Nasirli).
The official presentation of diplomas and the inauguration ceremony for the elected members will take place at the Second General Assembly, scheduled for the first half of 2026 in Beijing.
Media Contact:
Academician Emil Nasirli,
Chairman of the Media Relations Committee, Asian Academy of Sciences.
[e-mail: info@aa-sc.com]
The Asian Academy of Sciences has started its work in China
The Asian Academy of Sciences (AASc) is an international non-governmental organization headquartered in Hong Kong, China. It was established and registered (Registration Certificate number: 78606620) on the initiative of the Initiative Committee comprising distinguished scientists—including Chinese Top-Level National Talents, academicians of national academies of sciences, university rectors, and directors of research institutes—from China, Russia, India, Japan, Turkey, Azerbaijan, France, Kazakhstan, Pakistan, Iran, Georgia, Moldova, Kyrgyzstan, Uzbekistan, and other countries worldwide.
The Initiative Committee is chaired by Academician, Prof. Dr. Elchin Khalilov, "B-Category Top Level Chinese National Talent ". The organization’s name, "Asian Academy of Sciences", is officially registered with the International Standard Name Identifier (ISNI).
Academician Elchin Khalilov received a high government award in China
On July 08, 2025, Elchin Khalilov was awarded the WestLake Friendship Award, the highest government award for foreign scientists in Zhejiang Province, for outstanding scientific achievements during his time at Wenzhou University. This award was presented to E.Khalilov along with 50 foreign scientists with the state status of "National Talent of the Highest Category of China" from the USA, Japan, Canada, Russia, Italy, Germany, Great Britain, India, Israel, Pakistan and other countries. (https://www.wzu.edu.cn/info/1320/100567.htm).

Valery Tupolev, Vice President of the Russian Engineering Academy, received the highest award for foreign and engineering scientists from Zhengjiang Province
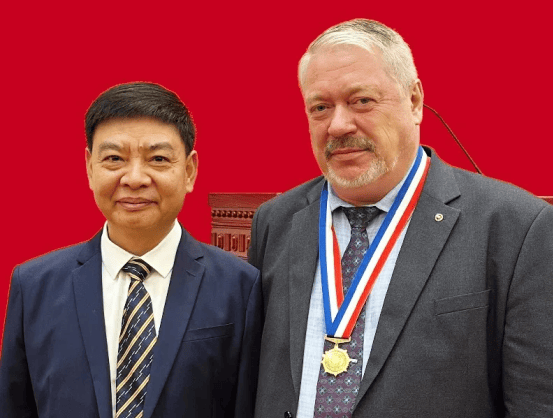
On July 8, 2025, the prestigious "West Lake Friendship Award" ceremony was held in Hangzhou, China. This important international award, which is presented every two years, was received by the representative of Russia, Valery Stanislavovich Tupolev, Vice-President of the Russian Engineering Academy (RIA), the Plenipotentiary representative of RIA and the International Academic Accreditation and Attestation Committee (IAAC) in China.
Valery Tupolev was recognized among outstanding scientists, engineers and public figures from around the world for his significant contribution to the development of the economy and society of Zhejiang Province, as well as for strengthening international relations.
The award was presented to Valery Tupolev by the Governor of Zhejiang Province, Mr. Wu Weibing. Together with the certificate, he received the honorary medal "West Lake Award 2025".
In his acceptance speech, Valery Tupolev emphasized the special role of the Russian-Chinese partnership in the technological progress and economy of both countries, noting that the interaction of technical communities is crucial for the successful development and well-being of the peoples of Russia and China. This high international award highlights Valery Tupolev's contribution to strengthening friendship and cooperation between our countries.
The Asian Academy of Sciences congratulates Valery Tupolev on this high government award from Zhengjiang Province and wishes him further outstanding success in his scientific and public activities.
TO THE MOON AND BEYOND
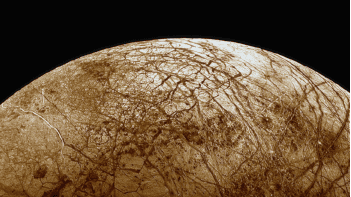
The global Artemis program is a NASA-led international space exploration program that aims to land the first woman and the first person of color on the Moon by 2025 as part of the long-term goal of establishing a sustainable human presence on the Moon. Additionally, the NASA mission called Europa Clipper, scheduled for a 2024 launch, will orbit around Jupiter and fly by Europa, one of Jupiter’s moons, to study the presence of water and its habitability. China’s mission, Chang’e 6, plans to bring samples from the moon back to Earth for further studies. The Martian Moons Exploration (MMX) mission by Japan’s JAXA plans to bring back samples from Phobos, one of the Mars moons. Boeing is also expected to do a test flight of its reusable space capsule Starliner, which can take people to low-earth orbit.
The R&D impact of Artemis extends to more fields than just aerospace engineering, though:
Robotics: Robots will play a critical role in the Artemis program, performing many tasks, such as collecting samples, building infrastructure, and conducting scientific research. This will drive the development of new robotic technologies, including autonomous systems and dexterous manipulators.
Space medicine: The Artemis program will require the development of new technologies to protect astronauts from the hazards of space travel, such as radiation exposure and microgravity. This will include scientific discoveries in medical diagnostics, therapeutics, and countermeasures.
Earth science: The Artemis program will provide a unique opportunity to study the Moon and its environment. This will lead to new insights into the Earth's history, geology, and climate.
Materials science: The extreme space environment will require new materials that are lightweight, durable, and radiation resistant. This will have applications in many industries, including aerospace, construction, and energy.
Information technology: The Artemis program will generate a massive amount of data, which will need to be processed, analyzed, and shared in real time. This will drive the development of new IT technologies, such as cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and machine learning.